An Overview of Technology and Innovation in Las Vegas
-

Drop anchors are internally threaded expansion fasteners used in solid conc...
When discussing Seiko’s legendary dive watches, the conversation often grav...

Η σημασία των πρακτικών υπεύθυνου τζόγου: Παίζοντας υπεύθυνα

Πλοήγηση στο νομικό τοπίο των διαδικτυακών καζίνο

A fertilizer is a synthetic or natural, chemical-based material which is us...
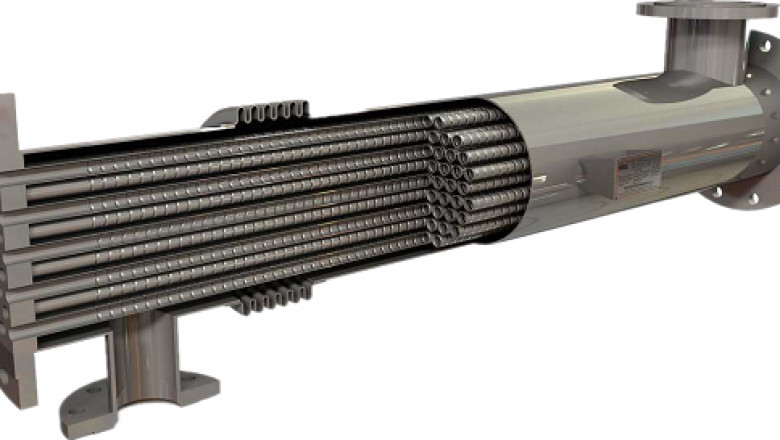
The heat exchanger market size is projected to reach US$ 39.11 billion by 2...

Learn how to start your USMLE Step 3 journey the right way with expert tips...

The Coating Additives Market is expected to register a CAGR of 4.7% from 20...











