What is a Myocardial Infarction?
A myocardial infarction, more commonly known as a heart attack, occurs when blood flow decreases or stops to part of the heart, causing damage to the heart muscle. The medical term for heart attack is myocardial infarction which comes from the Greek word “myocard” meaning heart muscle and the Latin word “infarctus” meaning dead tissue. Without enough oxygen-rich blood, the heart muscle begins to die. There are generally no warning signs before a heart attack and they can occur suddenly and without warning.
Symptoms of a Myocardial Infarction
The most common symptoms of a heart attack include:
- Chest pain or discomfort that feels like painful squeezing, heaviness, pressure or fullness. Chest pain is typically located in the center of the chest and lasts more than a few minutes.
- Pain radiating to the back, neck, jaw, shoulders or arms. This is known as referral pain and occurs frequently alongside chest pain.
- Shortness of breath with or without chest pain.
- Nausea, vomiting, indigestion or abdominal pain.
- Sweating, lightheadedness or fainting.
- A feeling of anxiety or dread that can mimic a panic attack.
- Fatigue or weakness.
Myocardial Infarction not everyone experiences chest pain and some heart attacks are “silent,” without any pain or obvious symptoms. Women are more likely than men to experience vague, non-specific symptoms. Anyone experiencing symptoms should seek immediate medical assistance.
Causes of a Myocardial Infarction
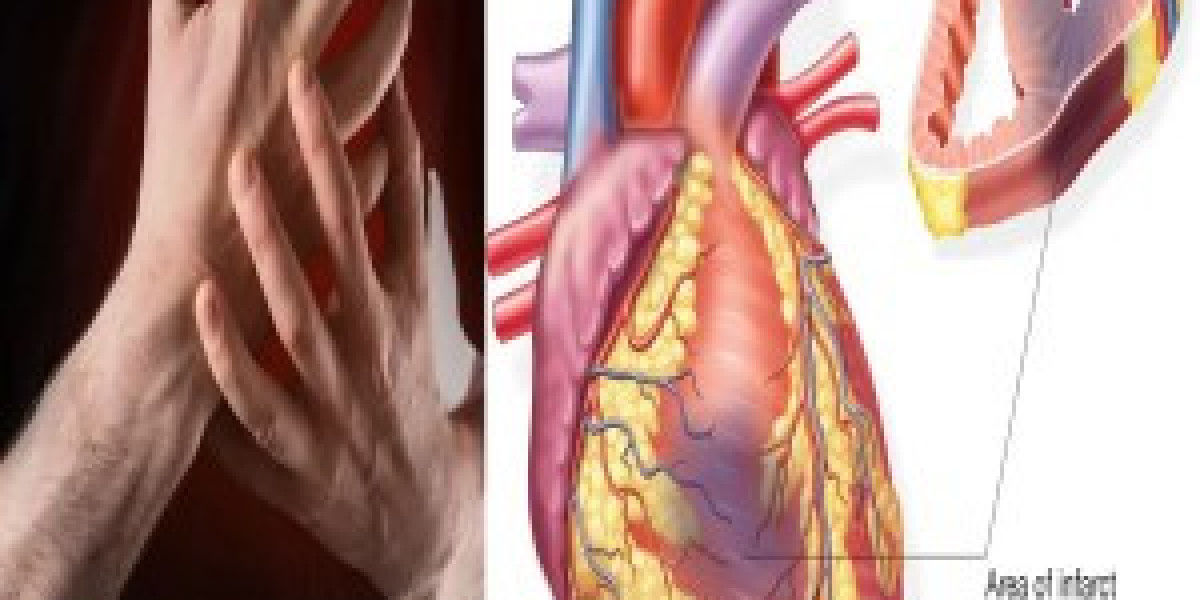
The underlying cause of a heart attack is the blockage of one or more of the coronary arteries due to a buildup of fatty plaque. The coronary arteries supply blood to the heart muscle itself. When the arteries become narrow or blocked, blood flow and oxygen are reduced or cut off to a portion of the heart, damaging the heart muscle.
The most common causes of blocked arteries include:
- Atherosclerosis: A gradual buildup of fatty plaque called atherosclerotic plaque inside the coronary arteries over many years. As plaque accumulates, the arteries narrow and blood flow is reduced.
- Blood clots: If a portion of accumulated plaque ruptures, a blood clot may form on top of it. If the clot is large enough, it can partially or completely block blood flow through the artery.
Certain risk factors such as high blood pressure, high cholesterol, diabetes and smoking increase the risk of plaque buildup and blood clots forming in the arteries of the heart.
Diagnosing a Myocardial Infarction
If a heart attack is suspected, several tests are used to help diagnose a myocardial infarction:
- Electrocardiogram (EKG or ECG): Measures and records the heart's electrical activity. It can show changes in rhythm and provide clues to damaged heart muscle.
- Blood tests: Levels of certain proteins are released into the bloodstream when heart muscle is damaged. Troponin and CK-MB levels rising or falling can help diagnose a heart attack.
- Echocardiogram: Uses sound waves to create images of the heart. It can show areas of poor heart muscle movement and estimates pumping ability.
- Imaging tests: Nuclear imaging scans using radioactive tracers or cardiac cardiac MRI can help locate regions of injured heart muscle not contracting normally.
The combination of symptoms, physical exam findings, EKG results and cardiac enzyme levels provide doctors with enough information to accurately diagnose a heart attack in the majority of cases.
Treating a Myocardial Infarction
Emergency treatment focuses on restoring blood flow to the heart and limiting the extent of damage:
- Oxygen: Supplied through a nasal cannula or face mask to help support heart and lung function.
- Aspirin: Given immediately to help prevent clot formation and additional blockages.
- Nitroglycerin or other vasodilating medications: Open coronary arteries by dilating blood vessels to increase blood supply.
- Beta blockers: Help control heart rate and reduce workload on the heart.
- Morphine: Relieves chest pain to help reduce stress to the heart.
- Coronary angiography: An X-ray procedure where a catheter is threaded to the heart to find blockages.
- Angioplasty and stenting: Inflates a tiny balloon to flatten plaque or inserts a metal mesh stent to prop open arteries during angiography.
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG): Reroutes blood flow around blocked arteries via vein or artery grafts during open heart surgery.
Additional treatments focus on control of heart disease risk factors and management of any heart damage effects going forward. Lifestyle modifications and medications are key to preventing recurrent heart attacks.
A myocardial infarction, or heart attack, is a serious, potentially life-threatening medical emergency caused by blocked arteries cutting off blood flow to the heart. The most effective emergency treatment involves rapidly restoring blood supply, controlling symptoms and limiting damage. While heart attacks often cause permanent changes, cardiac rehabilitation and risk factor management help recover heart function. Understanding the warning signs as well as available diagnostic tests and treatments could one day save your life or the life of a loved one experiencing a heart attack. Recognizing the symptoms and seeking prompt medical attention is critical.
Resources – The Role of Diagnostics in the Myocardial Infarction Market: Advances and Technologies
Recent development in Myocardial Infarction Market
Key Factors Driving Growth in the Myocardial Infarction Market
Innovative Treatments and Therapies in the Myocardial Infarction Market
Get This Report in Japanese Language:
Get This Report in Korean Language:
About Author:
Priya Pandey is a dynamic and passionate editor with over three years of expertise in content editing and proofreading. Holding a bachelor's degree in biotechnology, Priya has a knack for making the content engaging. Her diverse portfolio includes editing documents across different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. Priya's meticulous attention to detail and commitment to excellence make her an invaluable asset in the world of content creation and refinement. (LinkedIn- https://www.linkedin.com/in/priya-pandey-8417a8173/)