Peripheral vascular disease (PVD) and lymphoedema are two vascular conditions that can significantly impact a person's quality of life. Both conditions involve issues related to the circulatory system, with symptoms that may overlap but have distinct causes and treatment approaches. In this article, we will explore these conditions in detail, helping readers better understand their causes, symptoms, and the various treatment options available.
What is Peripheral Vascular Disease (PVD)?
Peripheral vascular disease refers to the narrowing or blockage of blood vessels outside of the heart and brain, primarily affecting the arteries in the legs and arms. This condition is typically caused by the buildup of fatty deposits or plaque in the blood vessels, which can restrict blood flow and lead to several complications. PVD is often associated with other cardiovascular diseases, such as coronary artery disease and stroke.
Causes of Peripheral Vascular Disease
The primary cause of PVD is atherosclerosis, a condition where fatty deposits (plaque) build up in the walls of the arteries. Risk factors that contribute to the development of PVD include:
Smoking: Smoking damages blood vessels and increases the likelihood of plaque buildup.
Diabetes: High blood sugar levels can damage blood vessels and make it easier for plaque to form.
High blood pressure: Constant pressure on the arterial walls can weaken and narrow the vessels.
High cholesterol: Elevated cholesterol levels contribute to plaque formation.
Age: As individuals age, the blood vessels become less flexible and more prone to narrowing.
Symptoms of Peripheral Vascular Disease
The symptoms of PVD can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Some common symptoms include:
Painful cramping in the legs, particularly during physical activity
Numbness or weakness in the affected limbs
Coldness or color changes in the skin of the legs or feet
Wounds or ulcers that are slow to heal
Reduced hair growth on the legs or feet
Shiny skin on the legs or feet
If left untreated, PVD can lead to severe complications, such as gangrene or amputation, making early detection and treatment essential.
What is Lymphoedema?
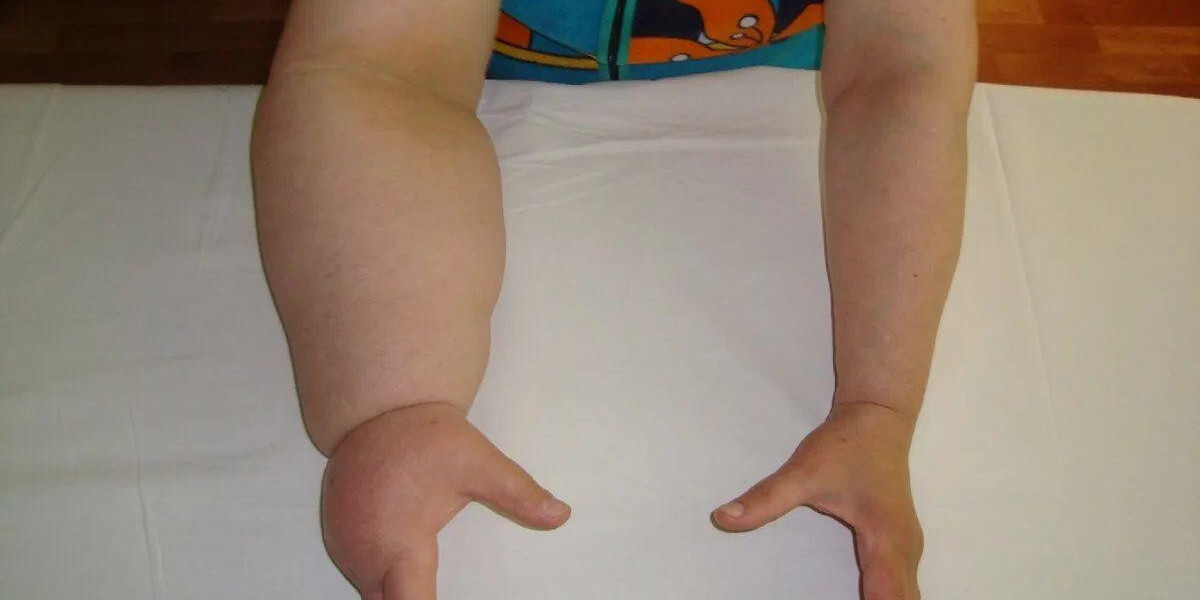
Lymphoedema is a condition characterized by the swelling of certain parts of the body, often the arms or legs, due to a build-up of lymph fluid. The lymphatic system is responsible for draining excess fluid from the tissues, but when this system is damaged or impaired, lymph fluid accumulates, leading to swelling. Lymphoedema is commonly seen in individuals who have had surgery or radiation therapy for cancer, but it can also occur for other reasons.
Causes of Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema can develop when the lymphatic vessels are blocked or damaged, preventing the normal flow of lymph fluid. Some causes include:
Surgery or radiation therapy: Especially for cancers like breast cancer or pelvic cancers, where lymph nodes may be removed or damaged.
Infections: Certain infections can damage lymphatic vessels, leading to lymphedema.
Congenital conditions: Some individuals are born with an underdeveloped or absent lymphatic system, leading to early-onset lymphedema.
Chronic venous insufficiency: When veins in the legs are unable to pump blood back to the heart, lymph fluid can accumulate in the lower limbs, contributing to swelling.
Symptoms of Lymphoedema
Lymphoedema typically begins with swelling that may worsen over time. Other symptoms include:
Swelling in the arms or legs, often beginning slowly and gradually increasing.
Tight or heavy feeling in the affected limb.
Skin changes, such as thickening or hardening of the skin.
Frequent infections in the affected area due to compromised lymphatic function.
Limited mobility in the affected limb due to swelling.
Like PVD, untreated lymphoedema can lead to severe complications such as infections and tissue damage, underscoring the importance of early intervention.
Treatment Options for Peripheral Vascular Disease and Lymphoedema
Both PVD and lymphoedema are manageable conditions, and a range of treatment options can help reduce symptoms and improve the patient's quality of life.
Treatment for Peripheral Vascular Disease
The treatment for PVD depends on the severity of the condition. Some common approaches include:
Lifestyle changes: Adopting a healthy diet, quitting smoking, exercising, and managing diabetes and blood pressure can help slow the progression of PVD.
Medications: Blood thinners, cholesterol-lowering medications, and medications to manage blood pressure can improve blood flow and reduce symptoms.
Surgical interventions: In severe cases, procedures like angioplasty (where a balloon is used to widen blocked arteries) or bypass surgery (to reroute blood flow around a blocked artery) may be necessary.
Endovenous procedures: In some cases, laser therapy or other minimally invasive procedures may be used to treat the affected vessels.
Treatment for Lymphoedema
Managing lymphoedema often involves a combination of therapies aimed at reducing swelling and improving lymph fluid drainage. Some common treatments include:
Compression garments: Specially designed sleeves or stockings can help control swelling by applying pressure to the affected area.
Manual lymph drainage: A form of gentle massage performed by a trained therapist to encourage lymph fluid movement.
Exercise: Light, regular exercise can improve circulation and fluid drainage.
Skin care: Proper skin care and hygiene can reduce the risk of infections, a common complication of lymphoedema.
Surgical options: In severe cases, surgery may be needed to remove excess tissue or repair damaged lymphatic vessels.
Conclusion: Moving Forward with Knowledge and Care
Peripheral vascular disease and lymphoedema, though different in their underlying causes, share similar outcomes when left untreated. Both conditions significantly affect circulation and fluid balance, leading to complications that can reduce a person's ability to live an active and healthy life.
It is crucial to identify the signs and symptoms of both PVD and lymphoedema early, as timely intervention can make a significant difference in treatment outcomes. With advancements in vascular and lymphatic care, including endovascular treatments and innovative therapies, patients have access to a wide range of options that can significantly improve their condition and quality of life.
If you are experiencing symptoms of either PVD or lymphoedema, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional or vascular specialist. At SG Vascular Centre, our experienced team of vascular surgeons is dedicated to providing holistic care for vascular-related conditions, ensuring that patients receive the best possible treatment tailored to their unique needs.