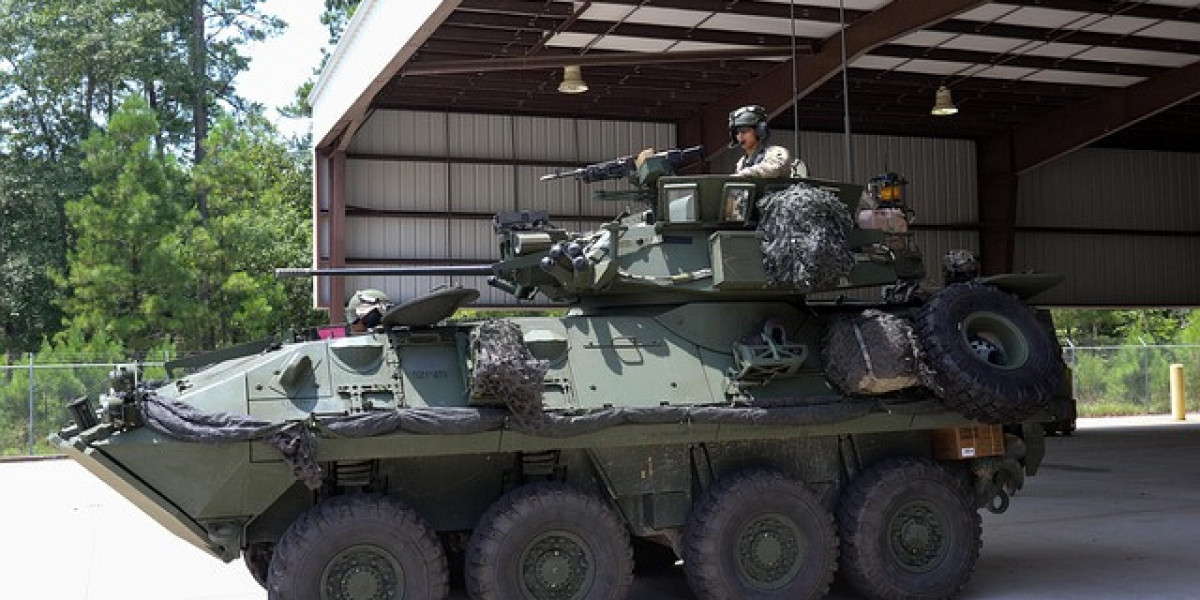
The First Armored Vehicles were developed during World War I as a response to the mass casualties caused by static trench warfare. In 1915, the British began developing the first tanks to break through enemy lines. These early tanks had crude armor but helped usher in a new phase of mechanized combat. Throughout the 1920s and 30s, militaries invested further in developing armored fighting vehicles like reconnaissance vehicles and armored personnel carriers.
By World War II, tanks had become far more advanced with thicker steel armor, improved engines and powerful cannons. Countries fielded various models designed for different roles on the battlefield. Advances in metallurgy, optics and suspension systems further boosted tanks' abilities in the post-war decades. Today's modern tanks, like the American M1 Abrams, feature armor strong enough to withstand direct hits from enemy cannons. They also have sophisticated infrared and laser targeting suites.
Diversifying the Roles of Armored Vehicles
While tanks remain central to mechanized warfare, the roles of Armored Vehicle have expanded significantly over the years. Vehicles like armored personnel carriers carry infantry into combat zones while protecting them from small arms fire and shell fragments. Many militaries also utilize armored troop carriers and armored cars for patrol and security operations in unstable regions.
Specialized Armored Vehicle Analysis support functions such as combat engineering, mine clearing and recovery/repair of disabled tanks. Unmanned armored vehicles equipped with sensors and weapons perform dangerous logistics, surveillance and attack missions. Airborne versions of armored carriers allow rapid troop deployment by parachute or helicopter. Coastal riverine forces use armored boats and amphibious vehicles for patrol and interdiction on waterways.
Commercial Applications
Armored technology is also used commercially for purposes like cash-in-transit, guarding critical infrastructure and providing security during civil unrest or natural disasters. Many banks employ purpose-built armored trucks fitted with multilayered bullet and blast-resistant materials to safely transport large sums of money. Bullion carrier vans transport precious metals like gold and silver between vaults and processing facilities.
Utilities employ armored vehicles for inspecting high-voltage power lines and repairing cables in hazardous zones. They give protection against potential electrocution threats. Cash centers, jewelry stores and other cash-intensive enterprises invest in specialized armored cabinets, safes and steel-reinforced vaults to securely house valuables on site. The South African police tactical response unit famously uses modified Casspirs, an armored personnel carrier originally designed for the military, for VIP protection and riot control duties.
Around the world, armored limousines provide bullet-resistant transportation for heads of state, diplomats and corporate executives during high-risk overseas visits or trips through unstable regions. Luxury variants boast features like run-flat tires, oxygen tanks, night-vision cameras and rear escape hatches. During the COVID-19 pandemic, some armored transports ferried medical workers and supplies to quarantine zones and hospitals overwhelmed by the crisis. In disaster relief efforts, armored vehicles deliver food and supplies to remote cut-off communities.
Vehicle Armoring Industry
The commercial vehicle armoring market exceeds $6 billion in annual revenues. Leading manufacturers include INKAS, Terradyne Armored Vehicles, Armormax, MSB and Plasan. Demand arises from government agencies, private security contractors, armored car operators and corporations engaging in at-risk business activities. Vehicle manufacturers also sell factory-armored models tailored for specific security applications.
Vehicle armoring typically involves adding hardened steel, composite armor or bullet-resistant glass components. Ballistic fabrics, ceramic inserts and kevlar panels further boost protection against small arms fire. Sensitive areas like fuel tanks receive additional defensive layers including metal mesh. Reputable firms conduct rigorous testing using assault rifles, shotguns and specialty ammunition to certify a vehicle's ballistic protection level before clients.
Modular designs allow for customizable solutions based on threat assessment for each end-user and operational region. From light scout cars to massive troop transports, today's armored vehicles shield lives in an era where violence occurs across both battlefield and urban settings. Pairing survivability with diverse mobility, they continue adapting to new dangers and purposes beyond traditional combat zones.
Get More Insights On- Armored Vehicle
Get This Report In Japanese Language
Get This Report In Korean Language
About Author:
Vaagisha brings over three years of expertise as a content editor in the market research domain. Originally a creative writer, she discovered her passion for editing, combining her flair for writing with a meticulous eye for detail. Her ability to craft and refine compelling content makes her an invaluable asset in delivering polished and engaging write-ups.
(LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vaagisha-singh-8080b91)