views
Introduction
The Turbidity Meter is a versatile and essential tool for measuring the turbidity or cloudiness of liquid samples. Turbidity is an important indicator of water quality, reflecting the presence of suspended particles that scatter or absorb light. Whether you are involved in water quality monitoring, environmental protection, industrial process control, or laboratory research, the ATO Turbidity Meter can provide accurate and reliable measurements to help you achieve your goals.
How to Use the Turbidity Meter
Preparation
- Check the Device: Ensure the turbidity meter is in good working condition. Inspect the device for any visible damage or issues.
- Calibration: Calibration is crucial for accurate measurements. Use standard solutions with known turbidity levels to calibrate the meter according to the manufacturer's instructions. ATO Turbidity Meters typically use formazin or polymer standards for calibration.
- Sample Collection: Collect a representative sample of the liquid you want to test. Use a clean, clear container to avoid contamination. Rinse the container with the sample water several times before filling it completely. For accurate results, take samples from multiple points if possible.

Measurement
1. Turn on the Device: Power on the turbidity meter and allow it to warm up for a few minutes to stabilize.
2. Select Measurement Mode: Some ATO Turbidity Meters offer different measurement ranges. Choose the appropriate range based on your expected turbidity levels.
3. Place the Sample: Pour the liquid sample into the sample chamber, ensuring it is filled to the designated level. Make sure the sample chamber is clean and free of fingerprints or debris. Insert the sample into the designated holder of the turbidity meter, ensuring the light path is clear.
4. Read the Measurement: Initiate the measurement process. The meter will automatically measure the amount of light scattered or absorbed by the particles in the sample and display the turbidity value on the screen. Record the displayed turbidity value once the reading stabilizes.
Data Recording
Record the Results: Note down the turbidity value displayed on the screen. Some ATO Turbidity Meters also provide options to store or export the data for further analysis.
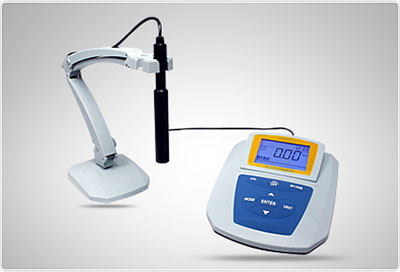
Caring for Your Turbidity Meter
Routine Maintenance
- Clean the Sample Chamber: After each use, clean the sample chamber thoroughly with distilled water to remove any residue. Dry it gently with a lint-free cloth. Avoid using abrasive materials or harsh chemicals that could damage the optical surfaces.
- Check the Light Source: Periodically inspect the light source for any signs of wear or damage. Replace it if necessary to ensure accurate measurements.
- Store Properly: When not in use, store the turbidity meter in a cool, dry place away from direct sunlight and extreme temperatures. Ensure the device is securely placed in protective cases or packing during transport to avoid damage.
Calibration and Validation
1. Regular Calibration: Calibrate the turbidity meter regularly using standard solutions to ensure its accuracy. Follow the manufacturer's guidelines for the frequency of calibration.
2. Validation: Periodically validate the instrument by comparing its readings with those of a known standard or another calibrated device.
Troubleshooting
1. Inaccurate Readings: If the readings seem inaccurate, check the calibration and ensure the sample chamber is clean and free of contaminants. Verify that the device is calibrated correctly and that the sample is representative.
2. Low Battery Indicator: If the low battery indicator lights up, replace the batteries immediately to avoid incorrect measurements. Ensure the device has sufficient battery power or is plugged in if it's a laboratory model.

Advanced Tips for Optimal Performance
1. Environmental Considerations: Ideally, operate the turbidity meter in a controlled environment with stable temperature and humidity conditions. Extreme temperature fluctuations or high humidity levels can affect the optical surfaces and electronic components.
2. Training and Documentation: Ensure that operators are adequately trained on the correct operation, maintenance, and troubleshooting of the instrument. Establish clear documentation and procedures for calibration, cleaning, and maintenance activities.
3. Interpreting Results: Understand the context of your measurements. Turbidity levels can vary significantly depending on the application. For example, drinking water should not exceed a turbidity level of 0.3 NTU in at least 95 percent of samples taken. Familiarize yourself with the standards applicable to your region or industry.
Conclusion
The Turbidity Meter is a powerful tool for measuring turbidity in liquid samples. By following the proper usage and care guidelines, you can ensure accurate and reliable measurements every time. Whether you are monitoring water quality, conducting environmental research, or controlling industrial processes, the ATO Turbidity Meter is an indispensable instrument in your toolkit. With regular maintenance and calibration, you can extend the operational life of your device and achieve consistent and accurate results.



Comments
0 comment