An Overview of Technology and Innovation in Las Vegas
-
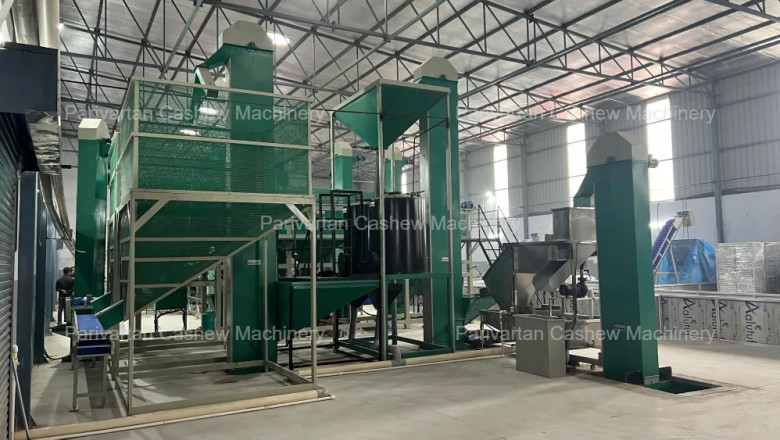

Boost efficiency and profits with a Fully Automatic Cashew Processing Plant...
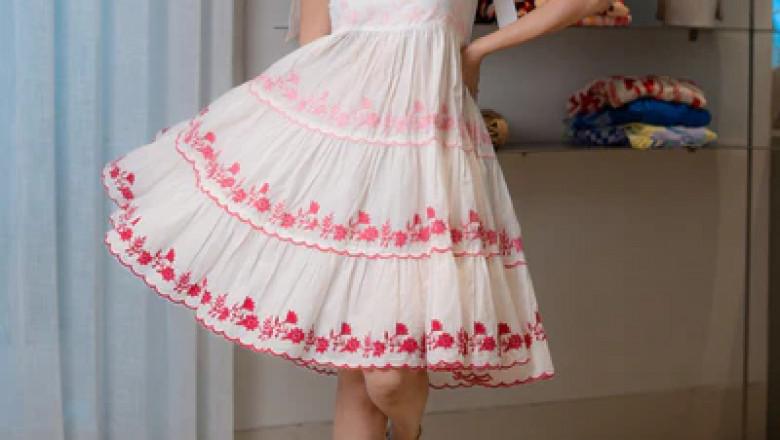

Discover Anrobee’s premium collection of designer dresses for women—featuri...
When it comes to professional piercing in a trusted setting, Warriors Ink i...

The Global Cloud API Market size is estimated to be valued at USD 2,392.8 M...

Discover how NBP Interiors blends technology with aesthetics to create smar...

This article breaks down the critical cryptocurrency development trends ent...

From improving security to simplifying user experience facial recognition s...

Feeling overwhelmed or low? Discover 10 signs you should see a psychologist...











