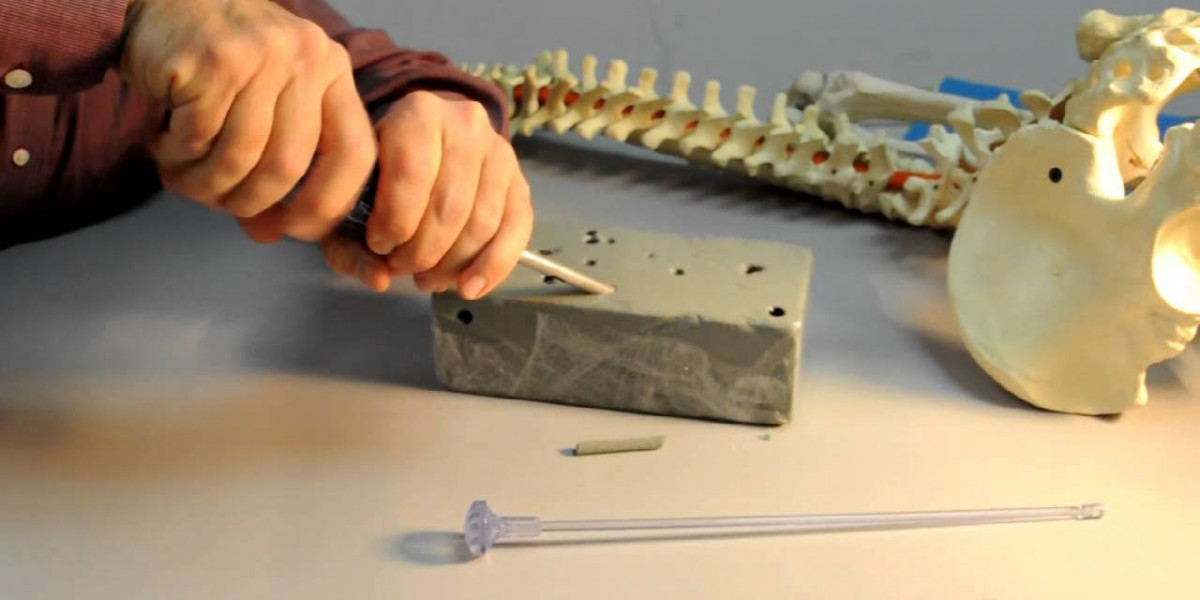
What is a Bone Graft Harvester?
A bone graft harvester is a medical device used in orthopedic surgery to efficiently collect autograft bone material from the patient's own bone during bone grafting procedures. These grafts are commonly used to fill gaps or replace missing bone following injuries, fractures, or to support implants like orthopedic screws and rods.
How Does it Work?
A Bone Graft Harvester works by using a hollow cutting cannula with a lateral opening and a plunger rod inside. To collect bone material, the surgeon makes an incision over the bone and inserts the harvesting cannula. The cannula is then pushed into the bone with a twisting motion to cut and collect a core of cancellous (spongy) bone. Once full, the cannula is withdrawn while keeping the plunger rod stationary. This enables containment of the bone graft within the cannula for easy transfer to the recipient site. Modern bone graft harvesters come with irrigation ports and guards to ensure safe and efficient collection of graft volume needed.
Advantages of Autologous Bone Grafting
Autologous or autograft bone, where graft material is taken from the patient's own body, is considered the gold standard for bone grafting procedures due to various advantages over alternative graft sources:
Osteoconductivity: Autografts have inherent osteoconductive properties that promote new bone growth due to the presence of native bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs) and other growth factors. This property helps achieve fusion at grafted sites.
Osteoinductivity: They are also osteoinductive as they contain pluripotent stem cells that can differentiate into osteoblasts and form new bone tissue. This induces new bone formation even when placed in non-bony sites.
Biocompatibility: Being "self-grafts", there is minimal immunological rejection compared to allografts (from a donor) or xenografts (from another species). This results in higher fusion success rates.
Structural support: Autografts provide immediate mechanical stability, weight bearing support and an ideal matrix for cellular infiltration and angiogenesis at grafted sites to facilitate healing.
Reduced disease transmission risk: As autografts eliminate the risks of disease transmission inherent with allografts or processed bone graft substitutes.
Areas of Clinical Application
Spinal Fusion: Harvesting local bone autograft from the posterior iliac crest is routinely done to fill interbody fusion cages or directly graft posterolateral fusion sites in spinal fusion surgeries for degenerative disc disorders, spine trauma and deformity corrections.
Orthopedic Trauma: Large bone defects from non-unions or segmental bone loss resulting from complex fractures are augmented with vascularised autografts harvested from fibular or tibial shafts.
Dental Implantology: To build vertical bone height and width in atrophic alveolar ridges, block bone grafts are harvested from the mandibular or maxillary blocks using bone graft harvesters and grafted at implant sites.
Maxillofacial Reconstruction: Contoured autografts are shaped and grafted after tumor resections to reconstruct large craniofacial bone defects following oncological resections.
Advantages of Bone Graft Harvesting
Ease of use: Modern bone graft harvesters featuring ergonomic handles and trigger action mechanisms make harvesting safe, quick and with minimal trauma compared to use of rongeurs or curettes.
Contained graft collection: The hollow cannula enables containment of graft volume collected with minimal bone loss or spillage compared to open surgical techniques.
Graft quality: Corticocancellous grafts retained have both the porous inner cancellous core containing pluripotent cells alongside the hard cortical rim bestowing structural strength - making it ideal for graft incorporation.
Minimal morbidity: The donor site at posterior iliac crest involves a small incision with minimal blood loss and reduced postoperative pain compared to open iliac crest block harvesting.
High yields: A single pass of the harvester can collect ~1-2cc cancellous bone - sufficient for most procedures. Multiple passes provide adequate volume if larger defects need filling.
In the bone graft harvesters present clear advantages for efficient and minimally invasive harvesting of structural corticocancellous autografts from the patient's own bone during orthopedic and craniomaxillofacial procedures. Their ease of use, graft containment and reduced harvest morbidity make them integral to achieving high fusion rates with autologous bone grafts - the gold standard for reconstructive bone grafting. Advancements in harvester design continue to optimize outcomes, making them an indispensable tool in the armamentarium of orthopedic and maxillofacial surgeons.
Get This Report in Japanese Language: 骨移植収穫機
Get This Report in Korean Language: 골 이식편 수확기
About Author:
Vaagisha brings over three years of expertise as a content editor in the market research domain. Originally a creative writer, she discovered her passion for editing, combining her flair for writing with a meticulous eye for detail. Her ability to craft and refine compelling content makes her an invaluable asset in delivering polished and engaging write-ups.
(LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vaagisha-singh-8080b91)