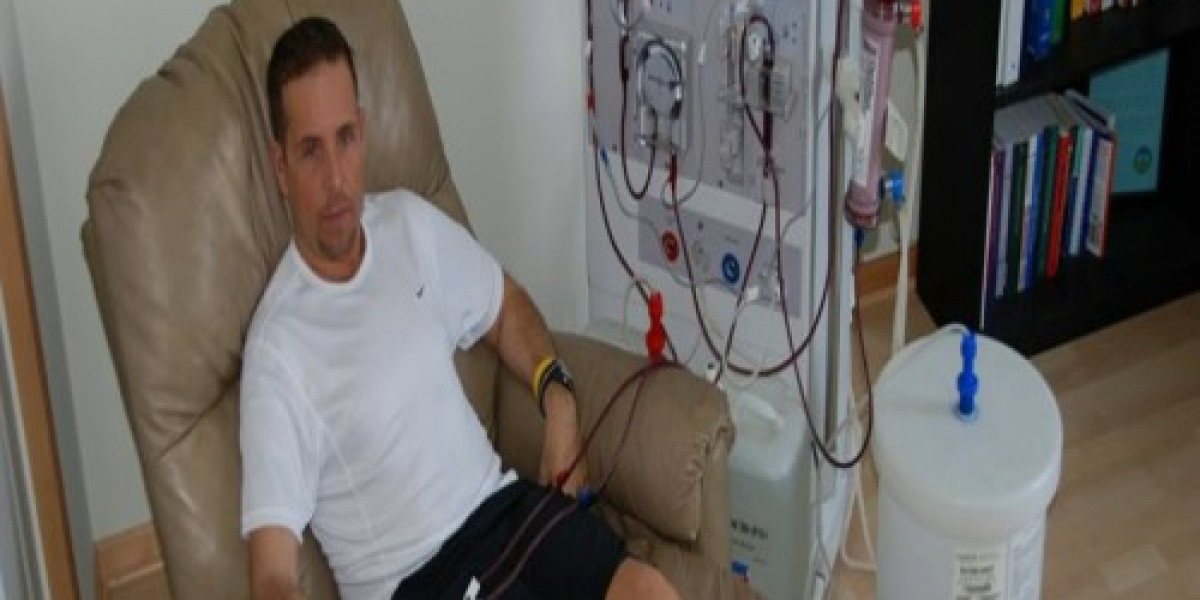
What is Peritoneal Dialysis?
Peritoneal dialysis (PD) is a treatment for kidney failure that uses the inner lining of the abdomen, called the peritoneum, to filter wastes and excess fluid from the blood. In PD, a cleansing fluid called dialysate is introduced into the abdomen through a small surgically placed tube called a catheter. Wastes and extra fluid move from the blood, through the peritoneum and into the dialysate. Then the used dialysate is drained out of the abdomen and fresh dialysate is put in.
How does Peritoneal Dialysis work?
Peritoneal Dialysis is the peritoneum acts as a natural filter. There are two types of PD: continuous ambulatory peritoneal dialysis (CAPD) and automated peritoneal dialysis (APD). In CAPD, exchanges of dialysate are done multiple times per day manually by the patient. They flush new dialysate into their abdomen through the catheter, wait for it to filter wastes from the blood, then drain the used dialysate. In APD, an automated machine does the dialysate exchanges during the night while the person sleeps.
Catheter Placement
The catheter needed for PD is surgically placed in the abdomen. It is usually placed in the lower part of the abdomen during a short surgery done under local anesthesia. The catheter has double cuffs that help keep it secure and prevent infections. It attaches to tubing that connects to bags of fresh dialysate.
Benefits of Peritoneal Dialysis
Some advantages of PD compared to hemodialysis include the ability to do treatment at home, more flexibility in daily routine, and no need to travel to a dialysis center multiple times a week. PD also avoids some complications of hemodialysis like risk of infections from the tubing used in dialysis machines. The continuous nature of PD provides more stable renal replacement therapy compared to intermittent hemodialysis treatments.
Potential Risks and Complications
Like any medical treatment, PD does carry some risks. The catheter site could become infected if proper sterile technique is not used during exchanges. The peritoneum could also become inflamed or infected rarely. Other possible complications include problems from the catheter like leakage, blockage or migration from the insertion site. High glucose levels in the dialysate long term may also increase the risk of infections. Careful sterile technique and monitoring by healthcare providers help minimize these risks.
Lifestyle on Peritoneal Dialysis
Once trained by nurses, most PD patients are able to independently do dialysis at home or work. Exchanges take around 30-45 minutes, and usually need to be spaced out throughout the day. Patients learn to disconnect and reconnect the tubing and flush the dialysate in and out of their abdomen. Exercise needs to be limited during exchanges to prevent leaks. Interruptions in treatment, like during travel, require planning with their healthcare team. Overall, PD allows greater flexibility than in-center hemodialysis.
Outcomes With Peritoneal Dialysis
Studies show that PD results in similar patient survival rates as hemodialysis over the first few years of treatment. However, long term outcomes over 5-10 years tend to be better with hemodialysis currently. These disparities are being addressed as PD techniques and technology continue to advance. Patient selection and commitment to therapy are also crucial to maximize results. PD remains an excellent option for kidney failure treatment, with outcomes dependent on individual clinical factors and dialysis adherence.
In the peritoneal dialysis is an effective renal replacement therapy for kidney failure that allows independence and quality of life. With proper training and support from healthcare providers, most patients are able to successfully manage their treatment at home. Outcomes continue to improve as new practices optimize this modality. With careful attention to risks, PD provides the benefits of kidney replacement without the need for frequent trips to a dialysis center. It remains a valuable treatment choice for suitable and committed patients with kidney failure.
Get This Report in Japanese Language: 腹膜透析
Get This Report in Korean Language: 복막 투석
About Author:
Vaagisha brings over three years of expertise as a content editor in the market research domain. Originally a creative writer, she discovered her passion for editing, combining her flair for writing with a meticulous eye for detail. Her ability to craft and refine compelling content makes her an invaluable asset in delivering polished and engaging write-ups.
(LinkedIn: https://www.linkedin.com/in/vaagisha-singh-8080b91)