What is Diethylene Glycol? A Deep Dive into the Versatile Chemical Compound
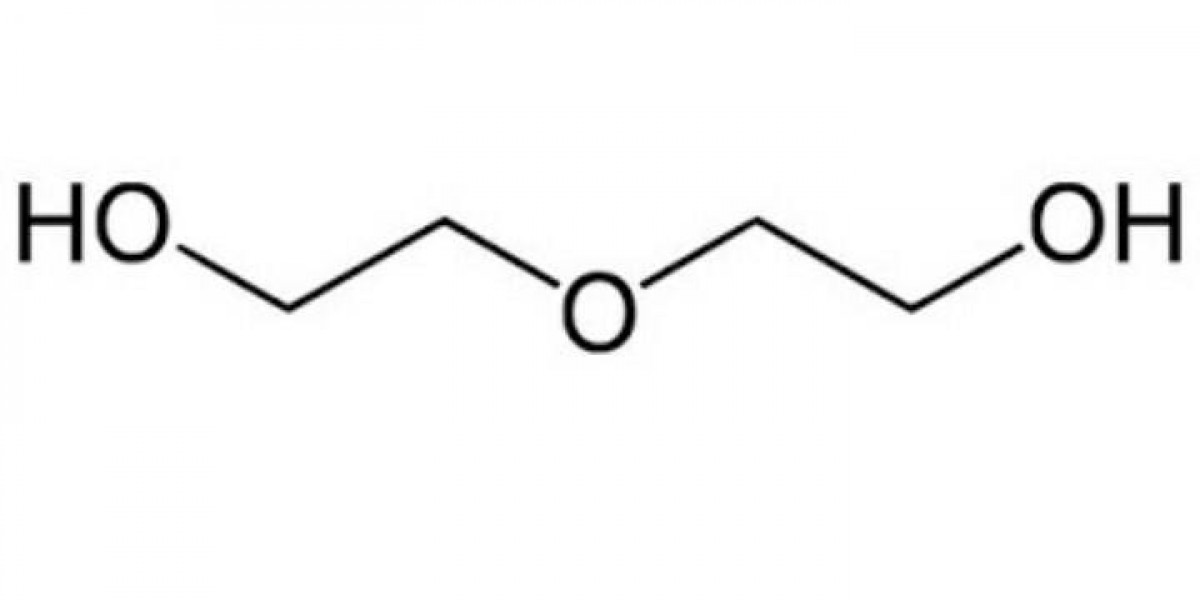
Diethylene glycol (DEG) is a colorless, odorless, and hygroscopic liquid that belongs to the glycol family of organic compounds. It is a widely used chemical in various industries due to its unique properties and versatility. Chemically, DEG is an alcohol with the formula (HOCH2CH2)2O, and it is produced by the reaction of ethylene oxide with water or ethylene glycol.
DEG has a slightly sweet taste and a syrupy consistency, making it an attractive ingredient in some applications. However, it is important to note that despite its sweet taste, DEG is toxic and should never be ingested. The compound has a boiling point of 245°C (473°F) and a freezing point of -10°C (14°F), allowing it to remain liquid at room temperature.
The Physical and Chemical Properties of Diethylene Glycol
One of the most notable properties of Diethylene Glycol is its ability to absorb moisture from the air, making it an effective humectant. This property is leveraged in various applications, such as in the production of plastics, resins, and inks, where it helps maintain moisture balance and prevents drying out.
DEG also has a low volatility, which means it evaporates slowly at room temperature. This property, combined with its high boiling point, makes it an excellent choice for applications that require a stable, long-lasting liquid. Additionally, DEG has a low freezing point, allowing it to remain liquid even at low temperatures.
Another important property of DEG is its ability to dissolve a wide range of substances, including water, alcohol, and many organic compounds. This solubility makes it a valuable solvent in numerous industrial processes, such as in the production of paints, coatings, and adhesives.
The Diverse Applications of Diethylene Glycol Across Industries
Diethylene glycol finds applications in a wide array of industries due to its unique properties and versatility. Some of the most prominent uses of DEG include:
Plasticizers and Resins
DEG is commonly used as a plasticizer in the production of resins, such as polyester and alkyd resins. Plasticizers are additives that increase the flexibility and durability of plastics, and DEG excels in this role due to its moisture-retaining properties and compatibility with various polymers.
In the production of polyester resins, DEG is often used as a co-monomer alongside other glycols and dicarboxylic acids. These resins are used in the manufacture of products such as fibers, films, and coatings. DEG helps improve the resin's flexibility, moisture resistance, and overall performance.
Brake Fluids and Antifreeze Formulations
DEG is a key ingredient in the production of brake fluids and antifreeze formulations for automobiles. In brake fluids, DEG acts as a lubricant and helps prevent corrosion of the brake system components. Its high boiling point ensures that the brake fluid remains stable and effective even under high-temperature conditions.
In antifreeze formulations, DEG is used alongside other glycols, such as ethylene glycol, to lower the freezing point of the coolant and prevent engine damage in cold weather. DEG's moisture-retaining properties also help prevent corrosion and scale buildup in the engine's cooling system.
Solvents and Chemical Intermediates
DEG's excellent solvent properties make it a valuable ingredient in various industrial processes. It is used as a solvent in the production of paints, coatings, inks, and adhesives, where it helps dissolve and disperse other ingredients evenly. DEG's low volatility and high boiling point also make it suitable for use in high-temperature applications, such as in the production of heat transfer fluids.
In addition to its use as a solvent, DEG also serves as a chemical intermediate in the synthesis of other compounds. For example, it is used in the production of morpholine, a chemical used in the manufacture of rubber accelerators, corrosion inhibitors, and pharmaceuticals.
Get more insights on, Diethylene Glycol
Get This Report in Japanese Language: ジエチレングリコール
Get This Report in Korean Language: 디에틸렌 글리콜
About Author:
Ravina Pandya, Content Writer, has a strong foothold in the market research industry. She specializes in writing well-researched articles from different industries, including food and beverages, information and technology, healthcare, chemical and materials, etc. (https://www.linkedin.com/in/ravina-pandya-1a3984191)